EVERYDAY LIFE OF DOMS OF BANARAS
December 31, 2020EVERYDAY LIFE OF DOMS OF BANARAS
December 31, 2020Sparkling International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research Studies
CRM STRATEGIES FOLLOWED BY APPAREL INDUSTRY OF INDIA
*Meenakshi Kaushik, **Sapna Dadwal, & ***Garima Bhati
*Professor, Accurate group of Institutions, Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh, India.
**Professor, St Andrews Institute of Technology & Management, Gurgaon (Haryana), India.
***Research Scholar, School of Commerce & Management, Lingayas University, Faridabad, Delhi, India.
Abstract
CRM is built on the philosophy of relationship marketing that aims to create, retain, develop and enhance relationships with customers as well as to enhance the customer lifetime value with the organization and organization’s profitability. Dynamic & Cutthroat competitive business environment has forced Apparel industry to implement such customer relationship management processes & practices which aims not only to attract but also to retain their old customers. The goal is to improve the customer experience with the organization so that it enhances satisfaction and loyalty which in turn will lead to increased profits. Customer relationship management is a wide business strategy adopted by most big organizations. In apparel industry requires a customer-centric business approach to support effective marketing, sales, service, and process. The study analyses CRM initiatives in the apparel Industry as the competitive environment for apparel organizations is changing rapidly. The apparel industry has emerged as a big component of the industrial sector in India and has been constantly adding to the revenue of our country. The apparel sector aims to serve the customer’s needs as per the latest fashion and trends.
Keywords: customer relationship management, apparel industry, fashion & trends
Introduction
The International business environment has changed as globalization is erasing the national boundaries and today companies are competing on a global market. This rapid change in the global environment puts high demands on companies to quickly be able to adjust to new situations in order to stay competitively strong. No company in this integrated world will remain unaffected by what happens in the world economy (Brake, Walker &Walker, 1995; Stanat, 2002).
From early 1980,s an alternative approach to marketing theory and practice was gaining power, namely relationship marketing. This shift from traditional marketing towards relationship marketing is occurring and several scholars are claiming this is a paradigm shift in marketing (Gummesson, 1997; Gronroos. 1997; Parvatiar and sheth, 1994). These changes have led the companies to switch to customer base structures. The key change is the advent of Customer Relation Management.
CRM stands for Customer Relationship Management. It is a process or methodology used to learn more about customers’ needs and behaviors in order to develop stronger relationships with them. There are many technological components to CRM, but thinking about CRM Software in primarily technological terms is a mistake. The more useful way to think about CRM is as a process that will help bring together lots of pieces of information about customers, sales, marketing effectiveness, responsiveness, and market trends. CRM (customer relationship management) is an information industry term for methodologies, software, and usually, Internet capabilities that help an enterprise manage customer relationships in an organized way. For example, an enterprise might build a database about its customers that described relationships in sufficient detail so that management, salespeople, people providing service, and perhaps the customer directly could access information, match customer needs with product plans and offerings, remind customers of service requirements, and know what other products a customer had purchased. CRM generally consists of:
- Helping an enterprise to enable its marketing departments to identify and target their best customers, manage marketing campaigns and generate quality leads for the sales team.
- Assisting the organization to improve telesales, account, and sales management by optimizing information shared by multiple employees, and streamlining existing processes (for example, taking orders using mobile devices).
- Allowing the formation of individualized relationships with customers, with the aim of improving customer satisfaction and maximizing profits; identifying the most profitable customers, and providing them the highest level of service.
- Providing employees with the information and processes necessary to know their customers understand and identify customer needs and effectively build relationships between the company, its customer base, and distribution partners.
From the above, it can be said that Customer relationship management (CRM) is a widely implemented strategy for managing a company’s interactions with customers, clients, and sales prospects. It involves using technology to organize, automate, and synchronize business processes—principally sales activities, but also those for marketing, customer service, and technical support. The overall goals are to find, attract, and win new clients, nurture and retain those the company already has, entice former clients back into the fold, and reduce the costs of marketing and client service. CRM describes a company-wide business strategy including customer-interface departments as well as other departments. Measuring and valuing customer relationships is critical to implementing this strategy.
Apparel Industry in India
“Indian apparel industry which is the second largest contributor in the retail industry after food and grocery is seeing some major shifts”. “Entry of international brands, changes in preferences from non-branded to branded, the fast-growing economy, the large young consuming population in the country has made India a highly lucrative market”. “India has the world’s largest youth population, which is becoming fashion conscious owing to mass media and social media penetration”. “This has opened unprecedented retail market opportunities”. “The promising growth rate of 9.7 percent makes the Indian fashion industry prominent in the retail sector”.” With a GDP growth rate of 7 percent, India has an edge over developed markets of the US, Europe, and Japan which are expected to grow at a rate of 2-3 percent. Favorable trade policies and increased penetration of organized retail among other factors contribute to making the Indian fashion industry attractive for investors (Source – http://www.indiaretailing.com)”
“Within the retail categories, apparel retail has demonstrated comparatively high receptivity towards corporatized retail”. “High penetration of corporatized retail in apparel has also paved the way to introduce more formal and systematic processes and procedures in operations, procurement and distribution”. “As a consequence, apparel retail market has managed to harness the advantages offered by modern management concepts leading to improved product offering, better customer management, and scientific supply chain management techniques”. “It is expected that apparel retail will continue to witness deeper penetration of corporatized retail beyond the major urban clusters and the increase in the demand of branded products (Source – http://www.indiaretailing.com)”
“The Indian apparel market can be broadly classified into men’s wear, women’s wear and kidswear. Currently, men’s wear holds the major share in the apparel market”. “It accounts for 41 percent of the total market”. “Women’s wear contributes almost 38 percent, while kidswear contributes 21 percent of the market”. “It is estimated that over the next decade women’s wear and kids wear will demonstrate high CAGR of 9.9 and 10.5 percent respectively, resulting in rising in market share of these categories”.” Both, men’s wear and women’s wear is expected to contribute 39 percent each to the total market in 2026, with kids swear accounting for the rest 22 percent (Source – http://www.indiaretailing.com)”
Literature Review
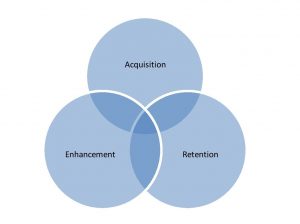
“Relationship marketing has been in vogue for more than two decades (Harker and Egan, 2006)”. “Its advocates see it as an emerging paradigm that promises much in the way of customer satisfaction and loyalty (Sheth and Parvatiyar, 1995; Gummesson, 1999). Pepper and Rogers (1995) define that CRM comprises three phases: acquiring, enhancing, and retaining. Each phase supports enhances the understanding between company its customers”.
The most basic definitions point to relationship marketing as attracting and keeping customers in the long term.” The aim is to convert buyer behaviour and status from fleeting casual encounters, through marketing interventions, to committed relationships (Varey, 2002). Relationship marketing advocates contend that marketing can no longer only be about developing, selling, and delivering products, where the emphasis was directed towards getting customers rather than keeping them. It is progressively more concerned with the development and maintenance of mutually satisfying relationships with customers (Buttle, 1996), and holds the promise of keeping customers loyal (Gummesson, 1994; Bulger, 1999). This pursuit is characterized by the quest to both fully understand and anticipate the customers’ needs, in a bid to develop long-lasting and mutually et al. 1999). A two-way or dialogue marketing communications approach is needed to support the establishment, maintenance, and enhancement of an interaction process if relationship marketing is to be successful (Sheth and Parvatiyar, 2000).
According to Bose (2002, p.15) CRM is defined as “an enterprise-wide integration of technologies and functions such as data warehouse, Websites, intranet/extranet, telephone support system, accounting, sales, marketing, and production”. According to Swift (2001, p.16), CRM is defined as “an enterprise approach for understanding and influencing customer behavior through meaningful communications in order to improve customer acquisition, customer retention, customer loyalty, and customer profitability”. From the above, it is clear that managing the customer plays a very important role in CRM. So the customer relation Management in general operationally defined by authors as a management process of acquiring customers by understanding their requirements retaining customers by fulfilling their requirements more than expectations and attracting new customers through customer-specific strategic marketing approaches.
The emergence of database and online communications technology (Dwyer et al, 1987; Pine et al; Palmer, 1999) opened the possibility of creating personal relationships with the mass market. In the words of Gronroos (1999) the database technology provides the means to engage the customer who wanted individual treatment”.
Research Methodology
“Research is a systematic inquiry aimed at providing information to solve problems (Cooper and Schindler, 2002:14)”. Differing requirements of information, availability of time, and need patterns have led to the developments of various types of research methods the need of any research method, however, remains the same–to get information the reason behind the use of any method for research should justify the generation of optimum results. This study is based on primary data, which has been collected through a questionnaire having statements to which respondents have to give their level of satisfaction ranging between 1-5 level and agreement ranging from strongly agrees to strongly disagree. Since it was not feasible to examine the entire universe the representative sample was selected from Delhi & Gurugram. Respondents were asked to fill questionnaire personally. The scope covers only three major multinationals of the apparel sector.
Objectives of the Study
As the title suggest the main objective of the present study is to know the role of CRM in the apparel industry of India. Other affiliated objectives along with the broad objective are-
- To know the perception of customers towards the CRM strategy in the apparel industry of India.
- To know the deficiency for the lower degree of customer satisfaction.
Data Analysis
To know the perception of customers towards organizations CRM strategy they were asked to evaluate each factor first on statements ranging from not at all important to extremely important and then they have to evaluate their satisfaction level with each factor on 1-5 scale. There are other questions also which will be evaluated on customer’s statements. The responses are analyzed by calculating the mean value and the results are presented in the subsequent discussion.
Table 1, 2, 3 & 4 gives the demographic profile–gender, age, occupation & Family income of the sample respondents. Table- 5 shows the variables of CRM in the food Apparel Industry and the mean % of consumer satisfaction level.
Table 1. Gender
| Gender | Frequency |
| Male | 100 |
| Female | 50 |
| Total | 150 |
Fig. 1 Gender

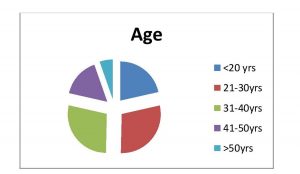
Table 2. Age
| Valid Category | Frequency |
| <20 yrs | 32 |
| 21-30yrs | 43 |
| 31-40yrs | 42 |
| 41-50yrs | 24 |
| >50yrs | 8 |
| Total | 150 |
Fig. 2 Age
Table 3. Occupation
| Valid Category | Frequency |
| Student | 54 |
| Self employed | 46 |
| Professional | 36 |
| Housewife | 10 |
| Sr. Citizen | 04 |
| Total | 150 |
Fig. 3 Occupation

Table 4. Family Income (Per Annum)
| Valid Category | Frequency |
| 1-2 lakh | 2 |
| 2-3 lakh | 31 |
| 3-5 lakh | 58 |
| >5 lakh | 59 |
| Total | 150 |
Fig. 4 Family Income (Per Annum)
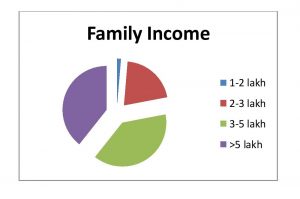
Table 5. Customer Satisfaction level for each factor in Apparel Sector
| Factors | Mean (Satisfaction Level) |
| Order processing speed | 3.8 |
| Degree of ease in getting Product | 3.2 |
| Pricing of the products | 3.4 |
| Quality of products | 3.2 |
| Customer Touch Points | 3.8 |
| Complaint Management | 2.8 |
| Quality of communication from company | 3.0 |
| Festival Schemes | 3.8 |
| Promotional Schemes | 3.9 |
| Reliability | 3.2 |
| Friendliness and politeness of employees | 3.5 |
| Accuracy of information | 3.1 |
| Product Variety | 3.5 |
| Complaint Management | 2.7 |
Findings
On the basis of the variables and statements in the questionnaire the following are findings-
- The study reveals that the customers are highly satisfied with the variables like order Processing speed, customer touchpoints, festival schemes, promotional schemes accuracy of information & product variety.
- The study also reveals that organizations need to improve in the variables like Complaint Management, Complaint Management Accuracy of information.
- The study also reveals that with some variables the satisfaction level is average. The organizations need to improve these.
Conclusion
The organizations in the Apparel industries need to focus on variables like Complaint Management, Complaint Management Accuracy of information to reap all benefits strategies & processes of Customer relationship management.
References
Berry, L.L., (2000), Relationship marketing of services- growing interest, emerging perspectives, in Sheth J.N., Parvatiyar, A. handbook of relationship marketing, Sage publications, London, 149-70.
Bulger.D. (1999). The evolution of Relationship Marketing : Reaching an Audience of One. Direct Marketing, 61(12), 54-59.
Buttle. (1996). Relationship Marketing, Theory and Practice. Paul Chapman Publishing Ltd., London
Grönroos, C., (1994). From marketing mix to relationship marketing. Toward a paradigm shift in marketing, Management Decision, 32(2), 4-32.
Gronroos, C., (1996). Relationship Marketing, Strategic and Tactical Implication, Management Decision, 34-3, 5.
Gronroos, C., (2000). Relationship Marketing- The Nordic School perspective in J.N. Sheth and A. Parvatiyar (eds.) Handbook of Relationship Marketing, Thousand Oaks, CA, Sage, 95-117.
Gummesson Evert. (1990). Service Design, The TQM Magazine, 2(2).
Gummesson Evert. (2002). Relationship Marketing and a New Economy, Its time for deprogramming, Journal of Services Marketing, 16(7).
Gummessone. (1999). Total Relationship Marketing: rethinking Marketing Management from 4P, st 30 R,s, Oxford: Butterworth Heinemann.
Peppers, D and Rogers, M. (1995). A New Marketing Paradigm: Share of Customers, not Market Share. Managing service quality, 5(3), 48-51.
Sheth J. and Parvatiyar, A. (1995). Relationship Marketing in Consumer Markets: Antecedents and consequences. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 23(4), 225-271.
Vary,R., (2002). Relationship Marketing, dialogue and Networks in the E-Commerce era, John Wiley&Sons, England.
To cite this article
Meenakshi Kaushik, Sapna Dadwal, & Garima Bhati. (2020). CRM Strategies Followed By Apparel Industry of India. Sparkling International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research Studies, 3(4), 1-8.